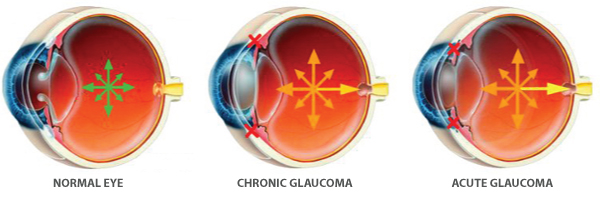
Glaucoma It is a disease in which the optic nerve is pressed or the blood supply is obstructed by the rise of the intraocular pressure, causing abnormalities of the optic nerve function. The optic nerve is a nerve that transmits the light received by the eye to the brain, so if there is a defect, the visual field defect appears, and at the end, the sight is lost.
Chronic (open angle) glaucoma is characterized by no symptoms at the beginning, and symptoms that appear to narrow the field of vision. In case of acute (closed angle) glaucoma, sudden increase in intraocular pressure may result in decreased visual acuity, congestion, eye sickness, severe headache and vomiting.